How To Download YouTube Videos Without Any External Tools?

YouTube is the one of the most popular video platform in the world. According to Wikipedia, YouTube has monthly 800 million visitors. More than 4 billion videos are viewed each day.
Downloading the YouTube videos are very common in these days. But YouTube doesn’t provide any default option to download YouTube videos directly. There are many sites, extensions, Software and tricks for downloading the YouTube Videos.
How To Download YouTube Videos Without Any External Tools?
Method 1:
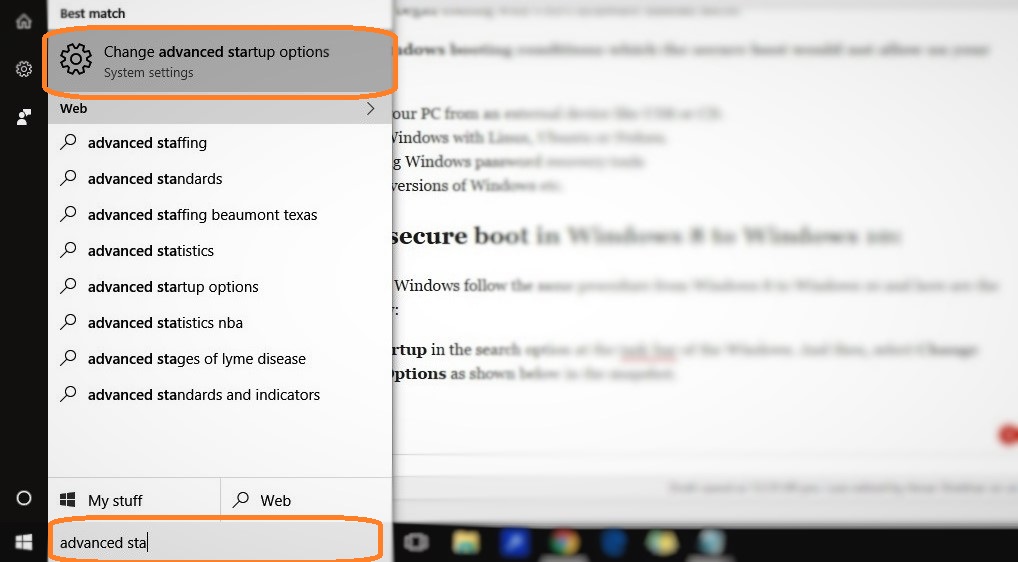
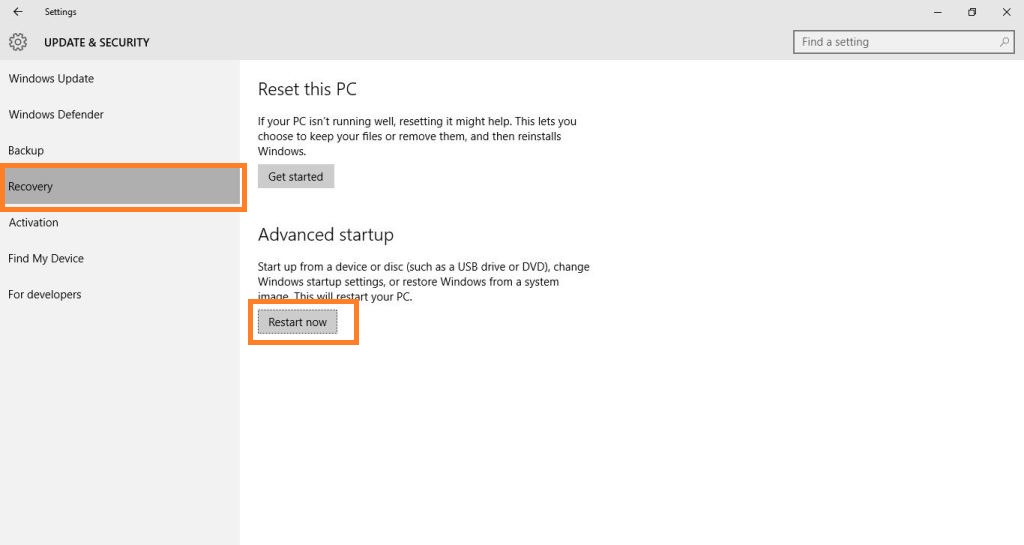
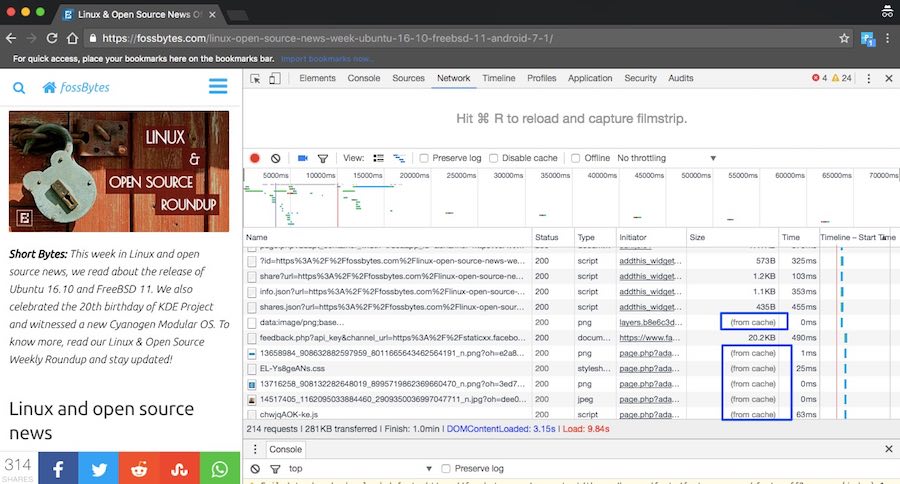
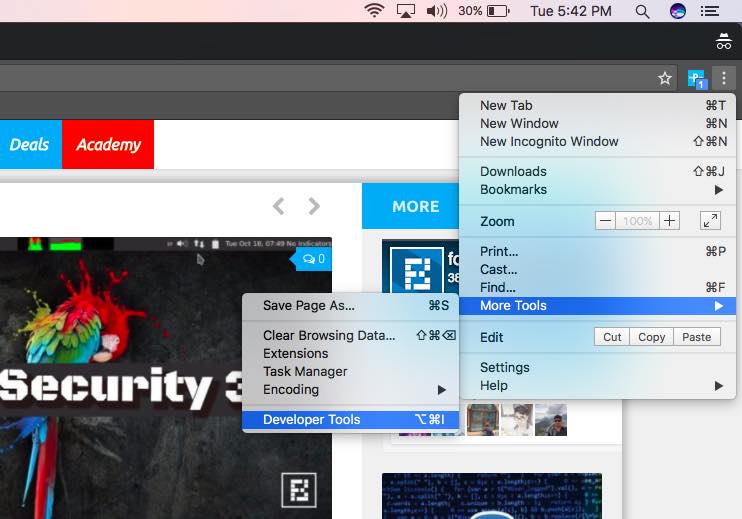
Step 1: Open the Developers tools in the browser and go to “Network.” If you are using Mozilla Firefox then use combine with “Ctrl+Shift+Q.”
Step 2: Now, click on “Media” in the “Network tool,” here you will see the HTTP requests made to media files, like audio and video files.
Step 3: Open any YouTube Video in browser, which you want to download. You will see the requests made by the YouTube Page to be audio &video files in the “Network tool.”
Step 4: Drift the cursor over the type column of each request in tool and look the media type:
- If you want the audio, look for “audio/mp4”.
- If you want the video, then look for “video/mp4”.
Step 5: Now, you will see “googlevideo.com” domain, click on it and copy the URL of the video, and open this video in the browser.
Step 6: Now, the video or audio will open in browser, right click on the page and select “Save As” to save the file.

Method 2:
Step 1: Open any YouTube Video in Browser, which you want to download.
Step 2: Now, you’ll see “www.youtube.com/watch?v….”
Step 3: Now, remove the “ube” from the “www.youtube.com/watch?v….” And press enter.
Step 4: You will see the “Record MP4/Mp3” option, select Mp3/Mp4 which you want to download. And click on the “Record MP4/Mp3” button, your video will be starting the download.

Hope you liked this tutorial. Leave a comment below if have any related issue with this. Don,t forget to share this post with friends.